
There are times when we struggle to apply a specific style to a specific element, but it simply doesn’t work, mainly because the element inherits CSS properties that have higher precedence than the code you’re writing. So you may need to understand overriding techniques to be able to do it.
Most commonly, developers use !important to override any kind of CSS property to save them time. But using !important is the wrong way to do anything. It could create more site-wide problems if used in global CSS. So use !important as your absolute last resort. There are many other ways you can inherit or override CSS properties.
CSS Inheritance:
Before we talk about overriding, let’s get a bit of understanding of how CSS inheritance works.
For any element, if apply set of rules is applied to style, the Same set of rules will be applied to all of its child elements. There is a simple way to inherit any property. Most of the time, we don’t specify the inherited word because it’s the default. We can override CSS or change it if we want to, by using an initial property. There is also an Unset property that works as inherited.
You can check my other article to get a detailed understanding of how CSS inheritance works.
Here is an example showcasing the inheritance between parent-child relations.
html,body{font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; color:blue;}
.parent1{color:brown;}
.parent2{color:tomato;}
.clild1-initial,.clild2-initial{ color: initial;}
.clild1-inherit,.clild2-inherit{ color: inherit;}
.clild1-unset,.clild2-unset{ color:unset;}
There is no noticeable difference between inherit and unset. But the initial property will reset the property to its default stage. In the case of color, it’s set to black. Having said that, let’s see what matters when we want to override CSS properties.
How To Override Inherited CSS:
Various properties might be inherited by an element depending on the Cascading order and the type of CSS used. To override these inherited CSS property values, we can use either of these methods:
- Define the selector in a higher cascading order
- Use a higher specificity selector
- Use!important as a last resort
!important keyword in CSS, overrides all the values in cascading order. But we can also override !important values with higher specificity !important values. So I always use !important as a last resort, otherwise it could create confusion.
Cascading order
CSS is called Cascading Style Sheets mainly because of its cascading (hierarchical ordering) nature. This means that if one element has two rules with the same precedence, the rule defined last will get the priority.
Let’s understand this using a practical example. Below are the styles ordered by their priority from lowest to highest.
1. Browser Defaults:
Each browser uses some set of default rules to style the content even if there is no style defined. For example, If we create a simple markup just using HTML and no CSS, different browsers will render that page with the browser’s default style. This can be shown in the Chrome Inspector tool or Firefox Dev Tools. Every browser has a set of changeable properties.
Default Browser style will look something like the example below:
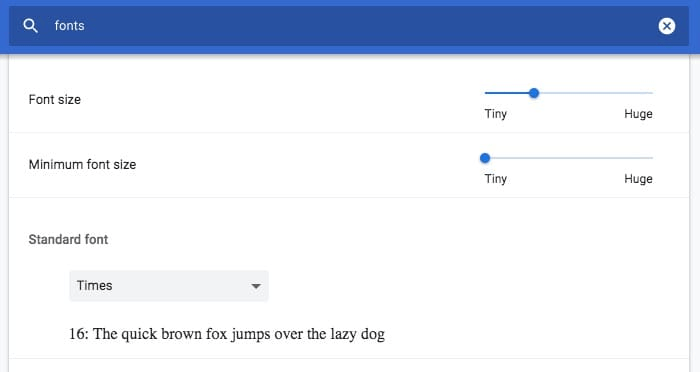
Chrome has settings to change Font Face and Minimum-Maximum font size.
Our technical experts can help fix any issue you are having with your website, regardless of its complexity.
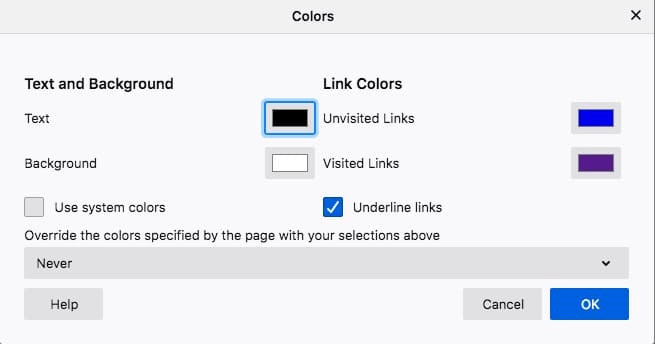
In Firefox, you can change Even Link Colors, background, and more.
How to override Browser Default CSS:
Just defining properties for the HTML tags will override the CSS style of the browser. You have to do this for every HTML element that you’re going to use in your project.
In the example below, the browser’s default CSS for html and body tags is overridden by the defined rule below, the body rule is further overridden by the body rule below because it’s last in the CSS definitions. This is how cascading works.
html,body{
margin:0;
Padding:0;
font-family: Arial, Helvetica;
font-size:100%;
color:red;
}
body{
color:blue;
}
A better way to do it: use reset.css (a reset CSS made by meyerweb ) to override and reset browser default styles.
Default Browser style will be overridden by reset.css, like the example:
2. External Style Sheets: Linked / Imported
Browser default is the easiest to override, but browser default is mostly being reset most of the time, and external or imported CSS takes the place of the default style. External CSS is just one method of adding CSS to HTML files, so it follows the same cascading behavior. The last imported or linked CSS will get precedence. And rules defined at last in the CSS file will have higher precedence. A small example to explain how cascading order works and how CSS selectors get precedence.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style1.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style2.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style3.css" />
In the above example, the style3.css will override all the properties within conflicting rules.
All 3 stylesheets have a style definition for the body, then the definition of the last CSS file will take over.
3. Internal Style Sheets: Embedded
Internal styles are added in the head part of the HTML file. So it gets higher precedence than external ones. But depending on the order of inclusion, the precedence changes.
Consider a case where we use both internal and external CSS together. Technically, internal CSS has higher priority, but because of its cascading nature, if we link or import external CSS after the internal CSS, the external will take over, even if internal CSS has higher priority.
<style>.tshirt__color{background:red;}</style>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style1.css" />
<style>.tshirt__color{background:maroon;}</style>
For cms like WordPress, internal CSS is added as the last element of the head so all internal rules can have higher precedence and can override CSS from an external stylesheet. Developers use this simple technique to develop themes. These internal styles override a set of rules using the CSS override method.
You can click on each checkbox to see it in action for example below:
For more complex layouts, CSS specificity comes into the picture, which uses a combination of various selectors to select a particular element. More info later in this article
Our technical experts can help fix any issue you are having with your website, regardless of its complexity.
4. Inline Styles
Inline CSS gets the highest precedence. Properties defined using this method will always override the browser default and external (until !important destroys it).
While creating dynamic apps, it’s hard to predefine a set of rules for a particular element because the element itself should be dynamically generated and you may want to override every single rule applied to it.
It’s good practice for designers to create rules for predefined elements and place them separately in CSS files, so when needed, developers can take advantage of inline CSS in their dynamic code without touching any internal or external CSS.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<style>.tshirt__color{background:green;}</style>
<div class="tshirt__color" style="background:red;"></div>
Look how inline CSS overrides all the other styles defined above the element.
I have an article that talks about how CSS can be added to HTML, talks about CSS Adding Techniques, and its benefits.
Internal Priorities
Despite its cascading nature, CSS cascading can be overridden by using a combination of selectors. This is something calculated on the type of selector and the number of selectors. Here is a simple CSS specificity calculator that shows how much weight a selector gets. The more selectors you choose, the more weight you get in precedence.
We covered how to distribute the weight of precedence in How to select anything in CSS article.
Just to summarise the specificity,
- Inline Style: It has the highest Specificity and will override other CSS with the same precedence.
- ID Selector: It has the highest precedence while using a single selector in internal or external CSS.
- Class Selector: Has lower precedence than ID.
- Tag Selector: Lowest precedence among all the selectors.
We’ll use the same example used in the above article to explain the initial priorities. We have added higher specificity using classes in the example below:
<style>
.parent1 .child1-initial{color:mediumorchid;}
div.parent1 .child2-inherit{color:teal;}
body .parent1#parent1 .child2-unset{color:slateblue;}
</style>
- The first selector has 2 classes, which will give the entire selector a specificity of 20
- The second selector has a div and 2 classes, which will give this selector specificity of 21
- The second selector has an id, 2 class selectors, and one tag, which gives a specificity of 121
These numbers will give you a better understanding of what gets priority. The higher the number, the more priority it gets.
!important
This is the easy way out for beginners, and it works well for small projects. But unless you know what you’re doing, you must avoid using !important. This will override every other rule applied to the same selector. So if not used wisely, it can cause site-wide damage. So I’d say never use !important.
!important to use the same rules of cascading and specificity to calculate priority if any conflict occurs. This could cause a lot of trouble in CSS.
.parent1{color:brown;}
.clild1{color:brown;}
.parent1.clild1-imp.red-colored,
.clild1-imp{color:red!important;}
.parent1.clild1-imp{color:blue!important;}
The above code uses !important to override defined properties for .child1
In the above example, we are overriding properties of the .child1 selector using !important. The .child1 block should have red color but it’s not because the property is being overridden by a higher specificity selector. We increased .child1’s specificity to override the blue color again. So the last child gets the red color because of its high precedence selector.
- Can override inline CSS
- Can override high specificity
- Can destroy the natural flow
- Can destroy Sitewide rule
Imagine you want to make a label red. So you added !important to the rule like label{ color:red !important;}, someone else working in the pile line won’t understand what to do because !important interrupting the natural flow, so we’ll create a rule like a form label{color:maroon !important} and we could end up creating multiple rules using !important to override CSS color property and it could disrupt the natural flow of CSS.
Where instead only a higher specificity rule was enough to solve the problem. There are tons of ways one element can be precisely selected and styled. To round off the entire case,
- Use specificity instead of using !important
- Never use !important when you’re writing a framework or CSS blueprint.
- Never use !important on site-wide global CSS.
Final Words:
One can use any of the mentioned techniques to override CSS. But the best practice is to consider using a cascading rule first. Using specificity second, and !important Never. !important can be used in the browser inspector to quickly check the impact of your rule. Or sometimes urgent quick fixes. But never use !important as a coding practice.




